Muscle gain and bulking are frequently misunderstood. Bulking may seem like just eating as much as you can, but a good bulking phase calls for a careful balance of scheduled exercise and nutrient-dense foods. The basic principles of bulking, safe methods for doing so, and an example diet plan that emphasizes natural foods to support muscle growth will all be covered in this article.
What is Bulking ?
Bulking is a planned time of excess calories used to gain muscle mass. The objective is to gain more muscle mass and strength, which frequently results in a little rise in body fat because of the extra calories. Bulking, as opposed to unstructured feeding, emphasizes striking a precise balance between protein, carbs, and fats in order to optimize muscle building and reduce fat gain.
Important Takeaways:
- Caloric Surplus: Eating more calories than you expend in order to build muscle.
- Macronutrient Balance: Prioritizing healthy lipids, protein, and carbs for energy and muscle repair.
- Progressive Overload: Using weight training to promote muscular growth and adaptability.
Types of Bulking:
Clean Bulking: Focuses on minimizing fat accumulation while maintaining a slight calorie surplus from nutritious meals.
Dirty Bulking: Makes it possible to consume more calories from a range of foods, including processed ones. In addition to muscular growth, this can result in considerable fat accumulation.
Clean bulking is mostly advised for beginners since it places an emphasis on wholesome eating, which is good for long-term health and can facilitate cutting (reducing extra fat).
How to Approach Bulking Safely ?
Determine Your Caloric Needs
To determine your baseline calorie requirements, start by figuring out your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE). Online calculators that account for age, weight, exercise level, and goals can be used for this. Aim for a daily caloric excess of 300–500 calories over your TDEE during bulking.
Make Protein Consumption a Priority
Protein is essential for both muscle growth and repair. Protein intake should be between 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight. Foods high in protein will promote muscle growth and inhibit muscle loss.
Include Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates give you energy for hard workouts and help you recuperate by replenishing muscle glycogen. Complex carbohydrates, such as brown rice, sweet potatoes, and oats, release energy gradually, providing you with long-lasting energy for exercising.
Look for Healthy Fats
The synthesis of hormones, such as testosterone, which is crucial for muscle building, depends on fats. Additionally, fats increase calorie intake, making it easier to meet your daily surplus. Pay attention to sources such as avocado, almonds, and olive oil.
Maintain Proper Hydration and Sleep
Hydration aids in muscle repair, nutrient absorption, and digestion. Depending on your level of exercise, aim for at least 8 cups of water each day. Since the majority of muscle healing happens while you’re sleeping, sleep is equally important.
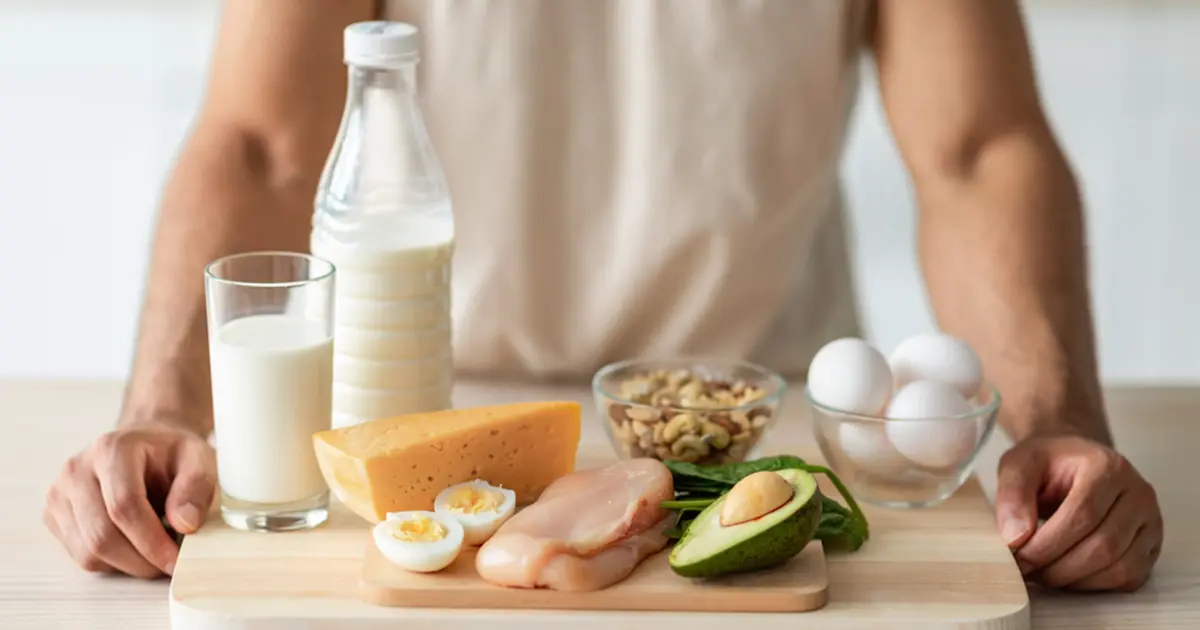
Bulking Nutrition Plan Using Natural Foods
Foods High in Protein
Lean Meats: Lean beef cuts, turkey, and chicken breast are all great low-fat, high-protein foods.
Fish: Protein and good fats, particularly omega-3s, are found in salmon, tuna, and trout.
Eggs: Packed with vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins, and high-quality protein.
Dairy Products: Milk, Greek yogurt, and cottage cheese provide calcium and protein to support healthy bones and muscles.
Legumes and Beans: Plant-based proteins with fiber that promote better digestion include black beans, chickpeas, and lentils.
Pros:
- Supplies the amino acids needed for muscle development and repair.
- Other nutrients are available from a range of sources (e.g., omega-3s in fish).
Cons:
- Eat red meat sparingly because it can contain a lot of saturated fat.
Complex Carbohydrates
Oats: Rich in fiber, which promotes steady energy release and helps with digestion.
Sweet potatoes: Rich in complex carbohydrates and vitamins A and C, they provide long-lasting energy.
Brown Rice: Staple in the diets of many athletes, it provides manganese, fiber, and B vitamins.
Quinoa: A complete protein that contains iron, fiber, and all of the essential amino acids.
Whole-Grain Pasta and Bread: Packed with fiber and B vitamins, whole grains give you energy for your workouts.
Pros:
- Helps with healing and exercise.
- Supplies fiber, which is good for the digestive system.
Cons:
- Consuming a lot of carbohydrates without getting enough exercise might cause weight gain.
Healthy Fats
Olive oil: Packed with heart-healthy monounsaturated fats.
Avocado: Rich in fiber, vitamins like potassium, and good fats.
Nuts and Seeds: Nuts such as flaxseeds, walnuts, chia seeds, and almonds provide fiber, protein, and lipids.
Coconut Oil: Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are rapidly digested for energy, are found in coconut oil.
Fatty Fish: Omega-3 fatty acids, which are good for muscle rehabilitation, are found in salmon and mackerel.
Pros:
- Promotes joint health and hormone production.
- Rich in calories, which aids in achieving bulking goals.
Cons:
- High in calories, therefore portion control is essential.
Example of a Bulking Daily Meal Plan
Breakfast:
- 3 scrambled eggs with spinach and tomatoes
- 1 serving of oatmeal with almond butter and banana
- Greek yogurt with berries
Lunch:
- Grilled chicken breast
- Quinoa salad with mixed vegetables and olive oil dressing
- Steamed sweet potatoes
Snack:
- Handful of almonds and an apple
- Cottage cheese with honey
Dinner:
- Salmon fillet with lemon and herbs
- Brown rice
- Roasted broccoli and carrots
Post-Workout Shake:
- Whey protein shake with milk or water
- 1 tablespoon of peanut butter
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Bulking
Excessive consumption of junk food: Quality is important even when a calorie surplus is the aim. Prioritize wholesome, nutrient-dense foods over processed snacks that are high in empty calories.
Ignoring physical activity: Even during a bulk, some exercise can enhance cardiovascular health and endurance.
Not Monitoring Progress: Keep a close eye on your weight, muscular growth, and energy levels so you may modify your diet as necessary.
What is the ideal duration for a bulking phase?
Depending on specific goals and how effectively a person responds to the diet and exercise routine, a bulking phase usually lasts four to six months. Since noticeable increases in muscle mass take time, it’s critical to strike a balance between the desire for quick muscular growth and the reality of steady progress.
Bulking Supplements (Optional)
While the main focus should be on natural foods, some supplements can support a bulking plan:
- Whey Protein: An easy and quick way to help muscles recover.
- Creatine Monohydrate: Enhances power and strength, enabling higher levels of exercise intensity.
- BCAAs: Promote muscle repair and may lessen weariness from exercise.
Conclusion
Building lean muscle through bulking needs commitment, consistency, and a balanced diet. To achieve consistent muscular growth, give priority to natural diets high in protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Keep in mind that bulking is about feeding your body in a way that encourages long-term muscular growth, not just about putting on weight. You can lay a solid foundation for developing the body you want with the right preparation and commitment.